Have you ever wondered how children learn to respond to the world around them? Sensory integration is the process by which the nervous system takes in messages from the senses and turns them into appropriate actions and behaviors. For children, this is important because it helps them with everything from focusing on schoolwork to playing with friends. Sensory integration techniques can be helpful, especially for children with sensory processing issues, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and ADHD.
The great news is that you don’t need expensive equipment to do this at home! Low tech assistive technology and devices don’t require electronic or digital components to function. They are accessible, cost-effective, and easy to implement at home, making them an excellent choice for many families.
In this blog, we will explore the essential supplies, materials, and activities that can help improve sensory integration, especially using low-tech assistive technology. These simple and affordable tools and techniques can be easily used at home to support your child’s sensory needs.
⚽ Tactile Supplies and Activities
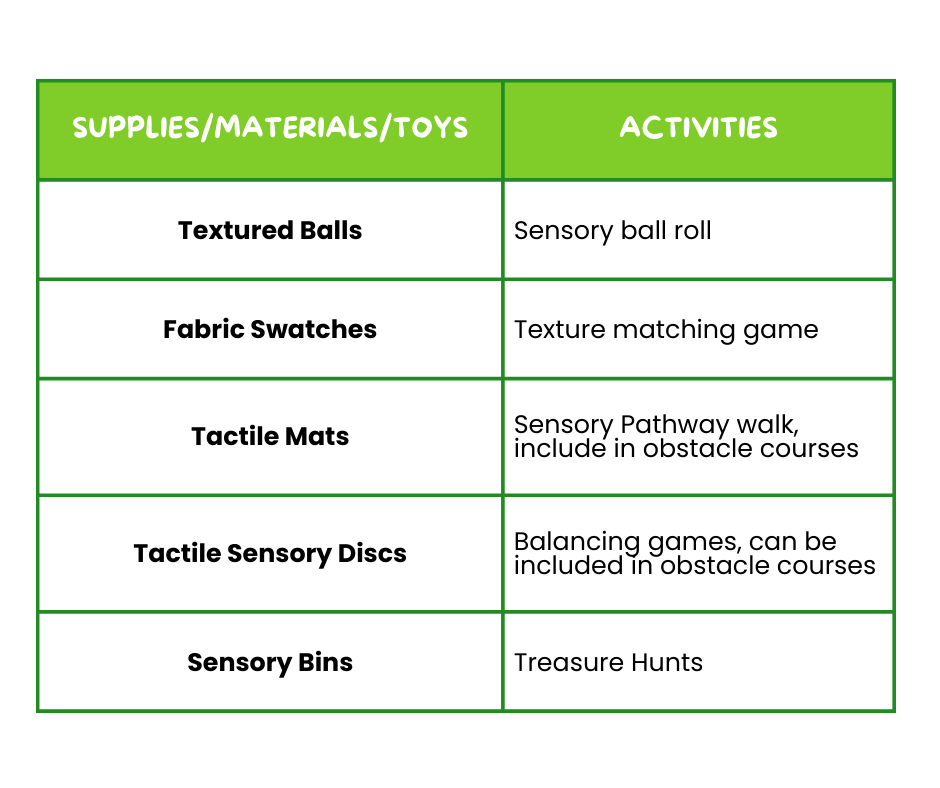
Engaging in activities with these tactile materials helps children develop their sensory processing skills, enhancing their ability to interpret and respond to different textures and sensations. These tools can provide calming or stimulation sensations depending on the child’s needs. For instance, textured balls and tactile mats can offer soothing tactile input that helps calm an overstimulated child, while sensory bins and tactile sensory discs can provide stimulating experiences that encourages sensory exploration.

🧩 Proprioceptive Supplies and Activities
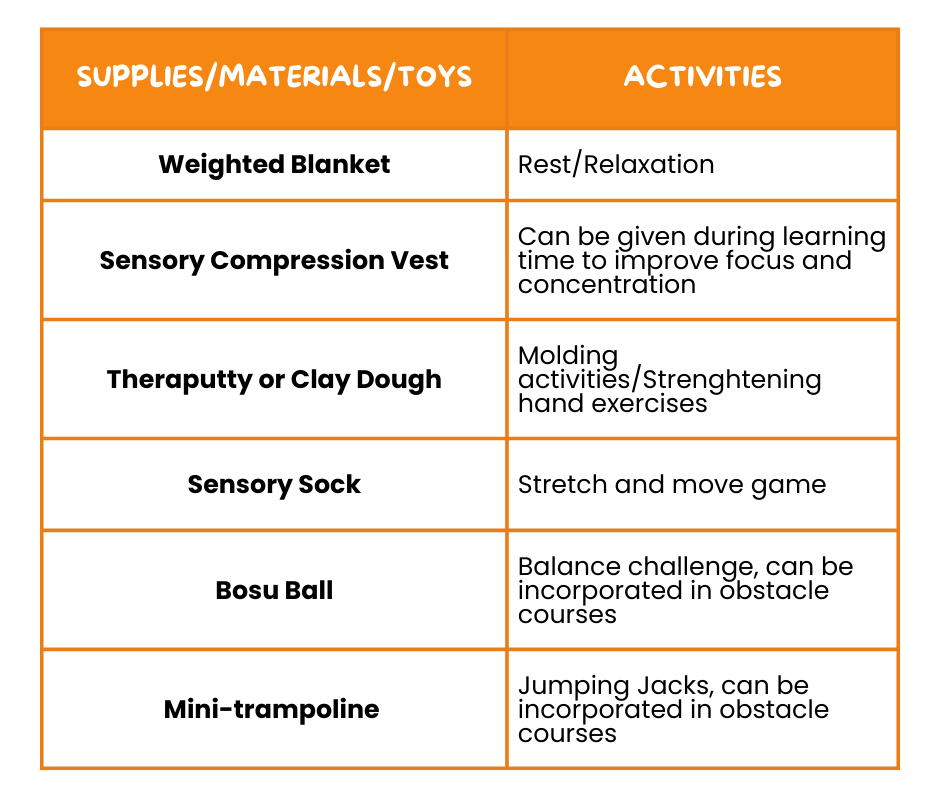
These materials provide deep pressure and sensory input that can help calm and organize your child. They’re great for helping your child feel more aware of their body and grounded.

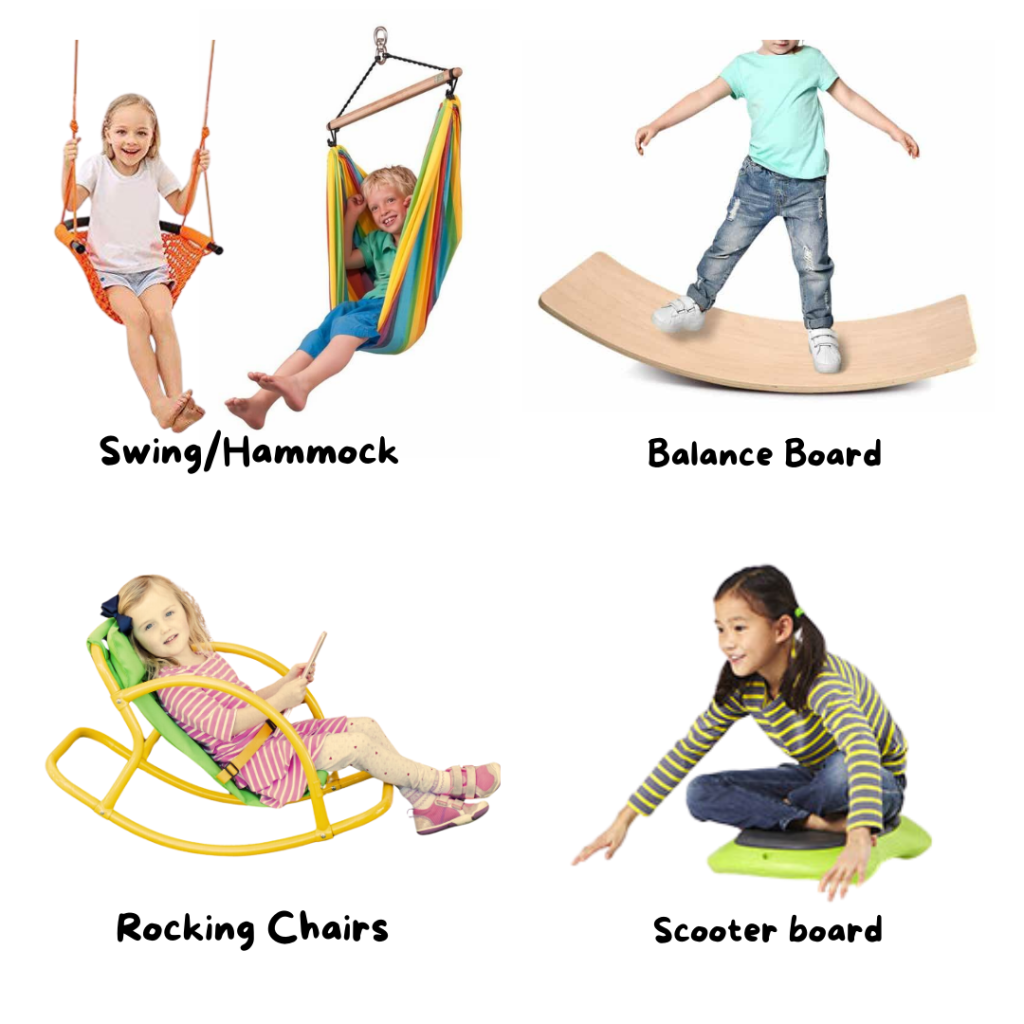
🎠 Vestibular Supplies and Activities
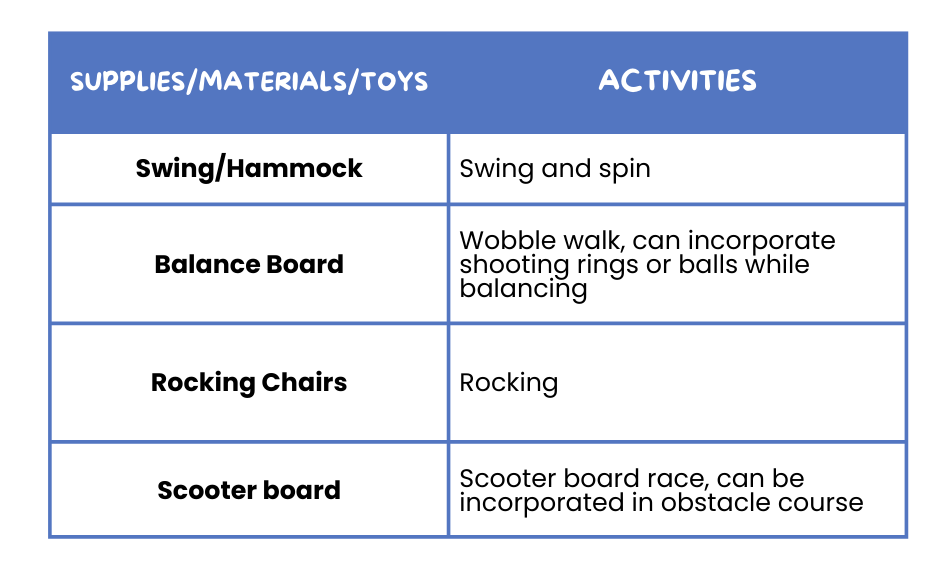
These supplies and activities can help children with their vestibular sensory processing, which is responsible for balance and spatial orientation. By engaging in these activities, kids can improve their coordination, and enhance their overall sensory processing, leading to better focus and daily functioning.

🎼 Auditory Supplies and Activities
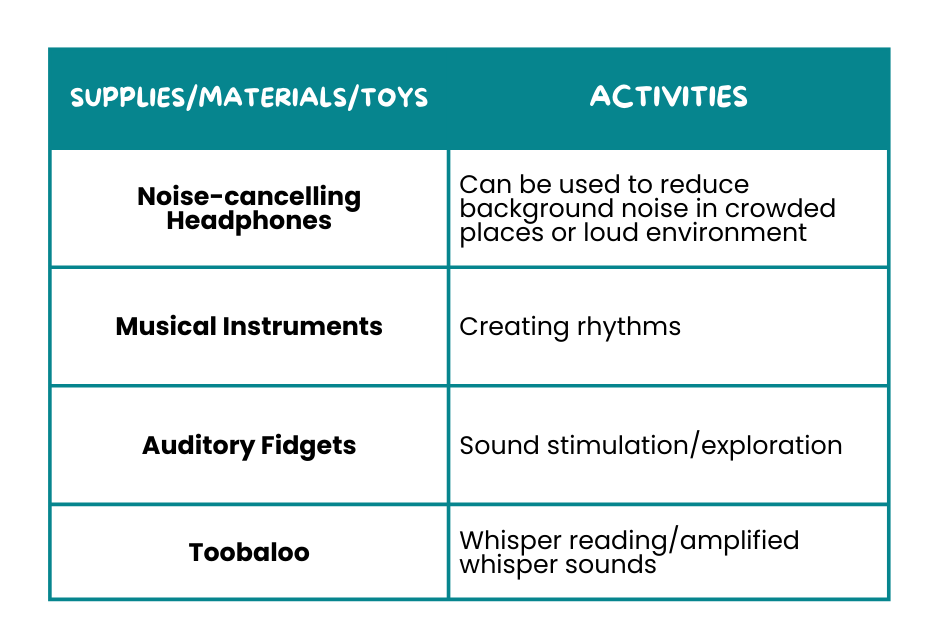
These auditory tools help children manage their response to sounds, making it easier for them to stay focused and calm. By using these tools, kids can either block out distracting noises or enjoy making sounds, improving their overall sensory experience.

🎨 Visual Supplies and Activities

These visual tools can help children develop visual sensory processing skills by engaging them in exploring colors, movements, and patterns. By interacting with these materials, children can enhance their visual perception, attention to detail, and ability to distinguish between different visual stimuli.

🥣 Gustatory Supplies and Activities
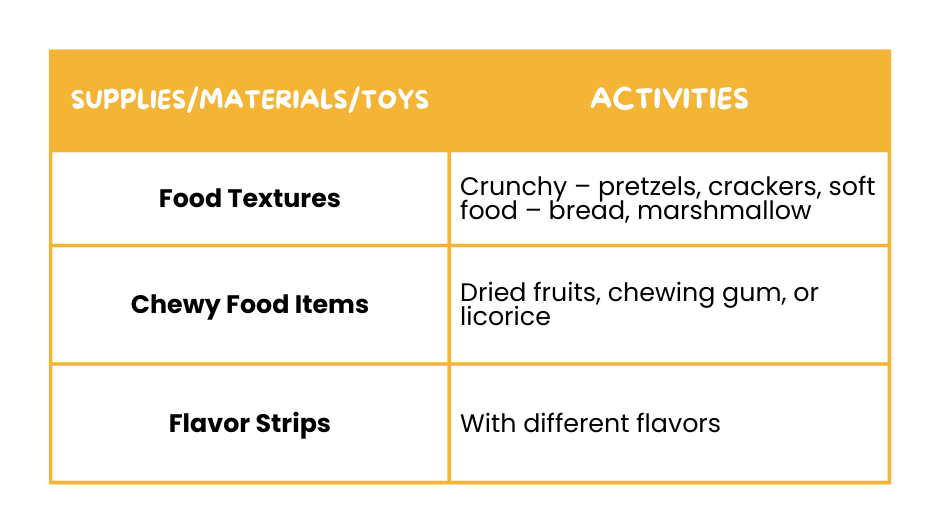
Different tasty and textured foods can help your child improve their sensory processing by exposing them to different flavors and sensations, helping them get used to and enjoy a wider range of foods. This can make it easier for them to handle different food experiences and feel more comfortable in various sensory environments.

🌼 Oflactory Supplies and Activities
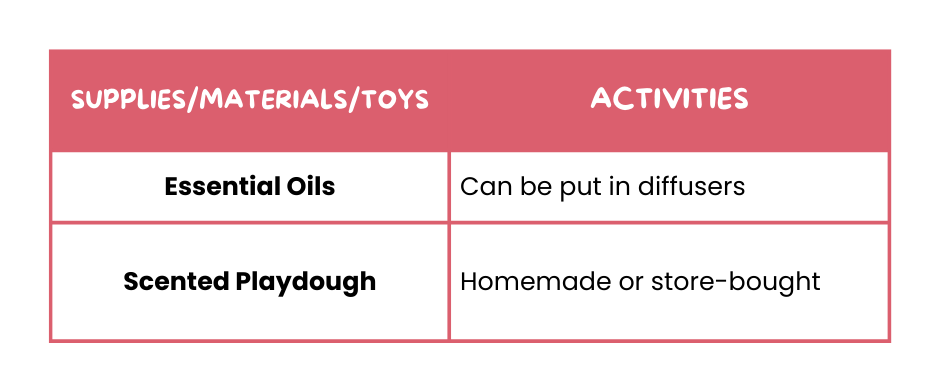
These scented supplies can provide stimulating and calming olfactory experience, improving their overall sensory processing, making them more comfortable and adaptable to different smells in their environment.

🛴 Creating a Sensory-Friendly Environment at Home
Designing a sensory-friendly environment involves creating spaces that support sensory needs:
Designing a Sensory Space: Choose a quiet, comfortable area at home, create a calming atmosphere with soft lighting and soothing colors to help your little ones feel more relaxed and regulated and reducing sensory overload.
Tactile-Friendly Spaces: Incorporate different textures through sensory walls or boards, use rugs and soft furnishings, and provide a variety of tactile materials.
Proprioceptive-Friendly Spaces: Set up a home gym or exercise area, include weighted items like blankets and cushions, and zones for heavy work activities.
Vestibular-Friendly Spaces: Install indoor swings or hammocks, create safe movement areas, and include balance and coordination equipments.
Auditory-Friendly Spaces: Use soundproofing techniques and create quiet zones for relaxation.
Visual-Friendly Spaces: Use soft lighting and maintain clutter-free areas to reduce visual overstimulation.
